If you are in the Ex-Im or Transport Business, it’s possible that you must have heard the word “Reverse Logistics.” And if you haven’t, we can understand! It is one of the most ignored parts of the Supply Chain. Even individuals in the Supply Chain tend to avoid it.
So here we are with the complete explanation of the topic.
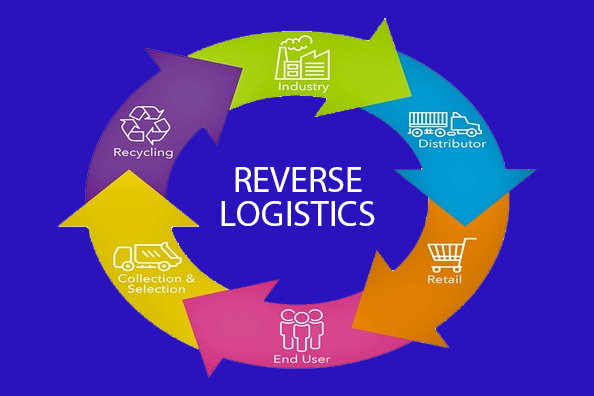
What exactly is Reverse Logistics?
Putting simply, Reverse Logistics is the process in the supply chain that deals with the return of any supplied goods to inventory. This includes any product returned by the end-user, inward disposal of packaging material, or recycling of the sold product.
Although neglected for years, the concept of Reverse Logistics is gaining popularity recently. Multiple research pieces suggest that the management of more than 40% of businesses thought Reverse Logistics is not important. Similarly, almost 35% of the supply chain executives claimed they do not have an efficient system to deal with this sector.
Why is Reverse Logistics important?
As business dynamics have changed significantly in the last decade, the importance of Reverse Logistics has sky-rocketed. With the rise of e-commerce on the global platform, more companies are now focusing on this sector.
Reverse Logistics holds significant importance for e-commerce due to the sheer size and volume of returned goods. Finding innovative and result-oriented solutions can help businesses deliver robust Customer Satisfaction and establish themselves as a leading Brand.
For some traditional stores dealing with gifts and books, the proportion of returns can vary from 3% to 20% of the total outward supply. But for some businesses, it might reach a whopping 55-60%. More surprisingly, these Reverse Logistics costs can be 3 to 4 times higher than the Forward Logistics.
Data clearly suggests even minor modifications in the whole chain can save millions for businesses around the globe. It can also indirectly benefit businesses by reducing storage costs and freight costs.
Types of Reverse Logistics
Reverse Logistics relates to any of the following activities after the initial purchase:
- Returns
- Remanufacturing
- Refurbishing
- Packaging
- Unsold goods
- End-of-life
- Rentals & leasing
- Repairs & maintenance
How is Reverse Logistics different than Traditional Logistics?
In general, the decision to initiate the logistics rests with the suppliers in the case of traditional logistics. Let’s understand the steps:
- Shipment to the distribution centers based on the sales forecast
- Shipment to the retail stores
- Supply to the end-users
On the contrary, the process is different from reverse logistics.
Let’s understand the steps:
- Return Request from the End-user
- Approval from the Return Processing Department
- Return to the Store
- Return to the distribution center
Now, let’s understand the difference between both of them with the definition:
Traditional Logistics:
“The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption to conform to customer requirements.”
Reverse Logistics:
“The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information from the point of consumption to the point of origin to recapture value or proper disposal.”
In simple words, in Traditional logistics, the goods are moved from the manufacturer to the end-user. In Reverse Logistics the process is done in reverse, the goods are moved from the end consumer to the manufacturer.
Process of Reverse Logistics
The process of Reverse Logistics is entirely different than Traditional Logistics. Unlike Traditional Logistics, where the shipper initiates the logistics activity, the end-user plays an important role in the process.
A classic example of reverse logistics is when a consumer returns a purchased product for a refund due to its quality or because it’s defective. The returned products may be resold or disposed of permanently. Although the business decides whether to initiate the reverse logistic activity, it is in the end-users response.
Once the activity is initiated, the product is collected and returned to the distribution center. At the same time, the information about the returned product like its condition, customer info, etc is shared with the return processing center.
This is where the system is flawed. As most of the existing systems are not designed to manage Reverse Logistics efficiently, they fail to collect the information accurately. Unfortunately, this information can be utilized to provide a better and more tailored shopping experience and satisfaction to customers. The results can be amazing which would help the business grow further.
Recommended Reading: Importance of Logistics in Supply Chain
With over two decades of expertise in Logistics and a long list of happy customers, Trans Asia Group can help you improve your global logistics, whether your company uses traditional or reverse logistics.
We are here to offer you hassle-free and customized logistics solutions, so you can do more with your business while we handle all the challenging tasks!
Contact us today or give us a call at +91 484 4096000 to talk to one of our logistics experts.